1. Hardware-Level Programming for Barcode Scanners
Some mid-to-high-end scanners support basic programmability through configuration barcodes, control commands, or firmware updates. Though this doesn’t involve coding, it’s a foundational way to control device behavior.
- ●Enabling/disabling specific barcode types (e.g., scan only Code 128, ignore QR codes)
- ●Switching scan modes (manual, auto-sensing, continuous scan)
- ●Formatting output data (adding prefixes/suffixes, inserting line breaks)
- ●Changing communication interfaces (USB HID, Serial, Bluetooth, etc.)
Common examples are:
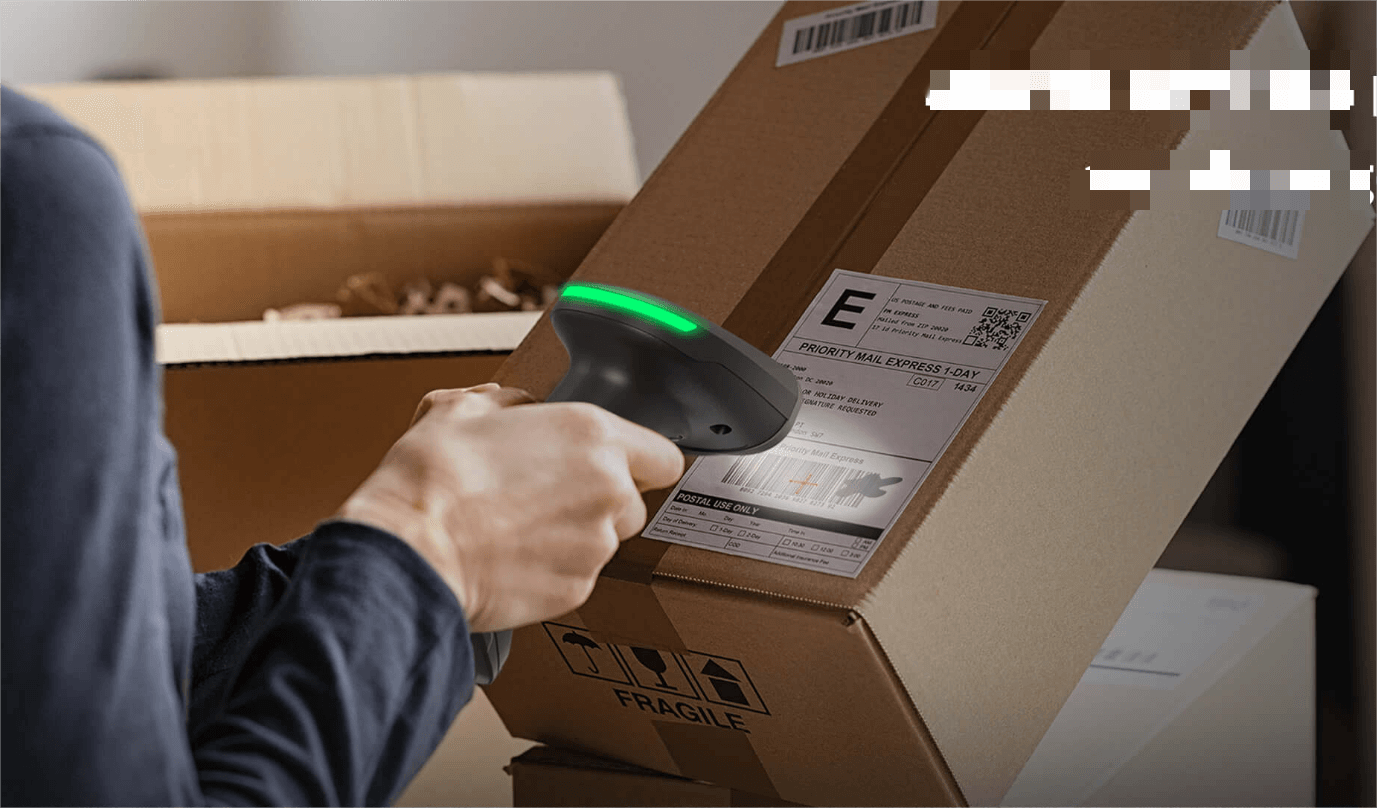

For instance, some iDPRT handheld scanners support quick setup via barcode commands to restrict scanning to 1D barcodes—ideal for e-commerce sorting and logistics label reading.
Some brands also allow real-time parameter control via serial commands, enabling external systems to interact with the scanner directly. This is especially useful for factory testing, bulk deployment, or embedded integrations.